World AIDS Day
Thursday, December 1st, 2022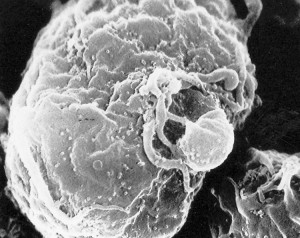
AIDS viruses reproduce in CD4 cells and circulate in the blood. In this electron micrograph of a white blood cell, AIDS viruses can be seen as the small white dots covering the cell’s surface.
Credit: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Today, December 1, 2022, is World AIDS Day. AIDS is the final, life-threatening stages of infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). HIV damages the immune system, the human body’s most important defense against disease. AIDS stands for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome or acquired immune deficiency syndrome. On this day, we honor over 40 million people who have lost their lives to AIDS and look ahead to ending the AIDS pandemic through research, healthcare, and community support. The World Health Organization reported that 38.4 million people were living with HIV across the globe at the end of 2021.
AIDS is a relatively new life-threatening disease. HIV is spread through sexual intercourse with an infected person or exposure to blood from an infected person, many times through shared needles used to inject drugs. At first, it mainly affected young adults. In the public imagination, the disease soon became associated with risky sexual behavior and with drug abuse. For all these reasons, efforts to address AIDS or to prevent the spread of HIV have at times faced unique social challenges. An infected pregnant woman can transmit HIV to her unborn child before and during the delivery, even if the woman shows no symptoms. An HIV-infected mother may also pass HIV to her baby through breast-feeding.
Since 1986, the international health community has worked to coordinate the global fight against HIV and AIDS. The World Health Organization’s Global AIDS Programme formed the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) in 1996. Since that time, UNAIDS has worked with other international partners to coordinate the global fight against HIV and AIDS. UNAIDS reported recently that one obstacle to ending AIDS around the world is gender inequality. Many girls and women live with HIV and AIDS without treatment and education to prevent infection. They report that in countries where girls do not receive an education, the rates of HIV infection are higher. UNAIDS also stated that in countries where same-sex relationships are criminalized the probability of infection is increased.
Many individuals and organizations have worked to increase public awareness of AIDS. The most active organizations include community-based groups and the American Red Cross. They hope that greater awareness will generate more compassion and support for people living with AIDS. They also hope to ensure adequate funding for HIV prevention, treatment, and research. One prominent project bringing attention to the crisis is the AIDS Memorial Quilt. Begun by the NAMES Project Foundation in 1987, the quilt consists of thousands of individually designed panels. The panels memorialize people who died of AIDS. The quilt has been displayed throughout the world.
Poor understanding of HIV has at times stoked public fears, leading many people with the virus to suffer unjustly. Some of the infected have lost or been denied jobs or housing. Others have been denied medical care and health insurance. Many children with AIDS were initially barred from attending school or playing on sports teams. To prevent discrimination, people with HIV and AIDS are often included under laws protecting the rights of people with disabilities. The United States government and some states have also strengthened laws safeguarding the confidentiality of medical records relating to HIV infection and AIDS.
Preventing discrimination against people with HIV is not only just—it also protects public health. When people can live without fear of discrimination, they are more likely to seek counseling and treatment. In many cases, such measures lead to earlier diagnosis and a reduction in risky behavior.
AIDS was first identified as a disease by physicians in California and in New York City, New York, in 1981. Doctors recognized the condition as something new because all the patients were previously healthy, young gay men. They sought medical care because they were suffering from otherwise rare forms of cancer and pneumonia. In 1982, the disease was named AIDS. Scientists soon determined that AIDS occurred when the immune system became damaged. They also learned that the agent that caused the damage was spread through sexual contact, shared drug needles, and infected blood transfusions.
AIDS occurs in every nation. In areas such as Africa south of the Sahara, Southeast Asia, and India, HIV transmission has occurred mostly among heterosexual men and women, particularly young adults and teens. Many developing nations carry enormous burdens of HIV infection. For example, the United Nations reports that in some parts of Africa, the infection rate may reach over 30 percent in some urban areas. The huge number of young adults dying of AIDS in Africa south of the Sahara has decreased overall life expectancy across the continent. A growing number of people have also become infected in countries with increasing drug use, such as Russia, China, and the nations of central Europe.




