Denisovans in Tibet
Wednesday, June 12th, 2019June 12, 2019
A recent reexamination of an important fossil discovery shows that Denisovans, a mysterious group of prehistoric people in Asia, lived in the high-altitude environment of the Tibetan Plateau long before the ancestors of modern Tibetans and Nepalese arrived. The fossil, a Denisovan mandible (lower jawbone) fragment, proves that these ancient humans were the first hominids to settle in that harsh environment where altitude sickness is a constant danger. The scientists studying the fossil also believe that modern people living on the Tibetan Plateau owe their survival to these Denisovan ancestors.
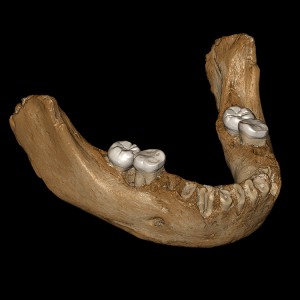
This virtual reconstruction shows details of the Denisovan mandible found on the Tibetan Plateau in 1980. It is some 160,000 years old. Credit: © Jean-Jacques Hublin, MPI-EVA, Leipzig
Chinese scientists recently reexamined the mandible fossil, which was excavated in Tibet in 1980. The jawbone fragment containing a few teeth was unremarkable. However, the scientists were hoping to determine the age of the fossil and extract proteins and genetic material using techniques that were not yet invented in the early 1980′s. The scientists were surprised when dating methods showed the fossil was about 160,000 years old. Scientists had previously believed that the early human populations alive at the time could not survive the harsh environment of the Tibetan Plateau.

The Denisovan mandible was found in this Tibetan Plateau cave, a tourist site and Buddhist refuge, in 1980. Credit: © Dongju Zhang, Lanzhou University
Analysis of proteins extracted from the jawbone fossil showed that it belonged to the mysterious Denisovans, a population previously known only from a few skeletal remains found in the Altai Mountains of southern Siberia. Denisovan DNA has similarities to that of the modern indigenous (native) peoples of Australia, New Guinea, the southern Philippines, and other Pacific Islands. Denisovans contributed up to five percent of the genetic material of some people living in these regions today.
Analysis of the Tibet jawbone shows that the Denisovans were well-suited to a high-altitude environment. They possessed a genetic adaptation that enabled them to withstand the physical effects of hypoxia (insufficient levels of oxygen in the blood) caused by high altitudes. Today, the indigenous people of Nepal and Tibet also possess this genetic adaptation. Scientists now believe that the modern inhabitants of the Tibetan Plateau inherited this adaptation from Denisovan ancestors of the distant past.