Statue of Liberty Museum
Wednesday, June 26th, 2019June 26, 2019
Last month, in May 2019, a new Statue of Liberty Museum opened alongside Lady Liberty herself on Liberty Island in New York Harbor. The museum details the history of the Statue of Liberty, from conception and completion to its current state. It also explains the evolving ideals of American liberty since the statue was completed in 1886, from the woman suffrage and civil rights movements to the welcoming of millions of immigrants from around the world. The museum also houses memorabilia and items that have been replaced on the statue, such as the famous original torch.

People admire the views from atop the Statue of Liberty Museum on May 16, 2019, the museum’s opening day. Credit: © Maria Kraynova, Shutterstock
Every year, some 4.3 million people take ferries to visit Liberty Island and the former immigration station on nearby Ellis Island. (Together, the islands make up the Statue of Liberty National Monument.) However, since the terror attacks of Sept. 11, 2001, the National Park Service has restricted the number of visitors who can enter the Statue of Liberty’s massive stone pedestal and travel up to the crown. A stand-alone museum, then, was created to accommodate all visitors to Liberty Island.
After the the abolition of slavery and the end of the American Civil War in 1865, the French politician and historian Édouard Laboulaye proposed the construction of a joint French and American monument celebrating the ideals of liberty. Laboulaye’s friend, the sculptor Frédéric Auguste Bartholdi, chose Liberty Island (then called Bedloe’s Island) for the statue’s location, and he began designing the massive monument. Construction of the statue—fully named Liberty Enlightening the World—began in 1875 at a workshop in Paris, and work on the pedestal began in 1884 in the United States. The last pieces of the statue arrived in New York in 1885, and the fully constructed statue and pedestal were dedicated in 1886.
The story of Lady Liberty’s torch is an interesting one. The torch arrived in 1876, ahead of the rest of the statue. It was displayed—along with the arm holding it—in Philadelphia and then in New York City. Originally, the torch was not meant to be illuminated from within. The gilded copper of the torch would reflect sunlight during the day, and lights were to be installed below it. By the time it was placed atop the statue in 1886, however, portholes had been cut in the torch to allow interior arc lights to be seen at night. The portholes were soon replaced with windows, and a sky light was added. At that time, visitors could ascend to the dizzying heights of the torch.
In 1916, floodlights were installed at the base of the statue and the torch lighting system was changed. People were no longer allowed in the torch or on the torch’s observation deck. Hundreds of windows were cut in the copper flame of the torch, and powerful lamps inside lit the torch.
In 1984, age and weather damage forced the removal of the original torch. The new torch, in place since 1986, followed the statue’s original plans and has no windows. Its flame is covered with gold leaf and glows with reflected light. The old torch toured the United States and was displayed in the Statue of Liberty’s pedestal before finding a home in the new museum.
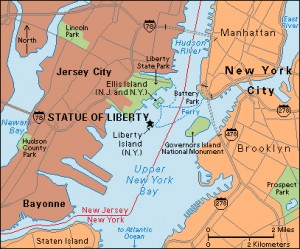
Click to view larger image
The Statue of Liberty National Monument includes Ellis and Liberty islands in Upper New York Bay. Credit: WORLD BOOK map
The Statue of Liberty Museum is accessible to all visitors of Liberty Island, and the grass-covered green building incorporates an environmentally responsible design and sustainable practices. The museum offers audio tours in 12 languages and ties together the American and international pursuits of liberty.
The popularity and symbolism of the Statue of Liberty have led to its replication in many parts of the world. The most famous miniature copies of the statue stand in France (naturally), Norway (where much of the statue’s copper was mined), Brazil, China, Israel, and Japan. Lego-brick Statues of Liberty stand among other world monuments at Legoland parks in Denmark and other countries. Finally, a “lazy” Lady Liberty sits (rather than stands) atop a building in Lviv, Ukraine.




