New Prehistoric Human Ancestor Found in Africa
Friday, March 30th, 2012March 30, 2012
Fossilized foot bones discovered in Ethiopia show that an unknown early human relative from East Africa had apelike feet more suited for life in the trees than for walking. Anthropologist Yohannes Haile-Selassie of the Cleveland Museum of Natural History in Ohio described 3.4 million-year-old fossils in the March 28, 2012, issue of the journal Nature. The scientists concluded that the fossils are from an early hominid. (Also called hominins, hominids are the scientific family that includes human beings and early humanlike ancestors.) However, the fossils are from a foot with long digits and an opposable big toe much like those in modern apes. (An opposable digit can be placed opposite another digit, such as the human thumb to the fingers.) These feature are useful for grasping tree limbs, but they make walking upright on the ground difficult. The fossils also indicate the creature’s foot lacked a distinctive arch, a necessary feature for efficient upright walking.
These new fossils were discovered at a site called Burtele in the Afar region of northeastern Ethiopia. The site is about the same age and only a few miles from Hadar, where fossils of Australopithecus afarensis were first discovered by anthropologist Donald C. Johanson in 1974. A. afarensis was an early humanlike creature known in part from a fossil skeleton nicknamed “Lucy.” The anatomy of Lucy and other A. afarensis fossils reveals that the creatures were small but walked upright on the ground like modern humans. Lucy’s foot anatomy shows a distinct arch and her big toe was aligned with the other four digits of the foot, the way it is in modern humans. These anatomical features allow for efficient walking on two legs on the ground. Preserved footprints at Laetoli, a site in northern Tanzania that also preserves fossil remains of A. afarensis prove that these creatures walked much the same way as modern humans do as long as 3.7 million years ago.
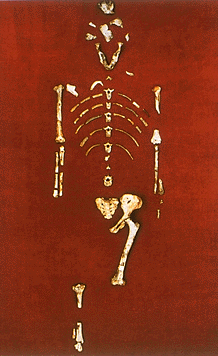
The skeleton of "Lucy," a prehuman ancestor that lived about 3.2 million years ago, has revealed that this australopithecine walked in much the same way as modern humans do. Lucy lived at about the same time as a newly discovered prehuman species that lived mostly in the trees. (Institute of Human Origins)
Scientists cannot assign a species name to the Burtele fossil without finding additional parts of the skeleton, such as the skull or teeth. But the fossils demonstrate that Lucy and her kind were only one of perhaps several hominid species that inhabited the forests and grasslands of East Africa more than 3 million years ago. Each species was adapted to a different habitat and likely had different anatomy and behavior, including how they moved around. As Lucy and her kind strolled along the plains, their distant cousins may have watched them pass from a perch in the trees.
Additional World Book articles:
- Evolution
- Prehistoric people
- Rethinking the Human Family Tree (a special report of historic interest)
- Anthropology 1974 (Back in Time article)
- Anthropology 1983 (Back in Time article)


