Carbon Dioxide Levels in Earth’s Atmosphere Reach Record Levels
Tuesday, December 6th, 2011Dec. 6, 2011
The amount of heat-trapping carbon dioxide (CO2) being pumped into Earth’s atmosphere jumped to record levels in 2010, according to the annual report by the Global Carbon Project (GCP). The GCP is an international collaboration of scientific organizations. The report said that the emissions rose by 5.9 percent, more than one-half billion tons of carbon. It was the largest annual increase since scientists began taking precise measurements of CO2 emissions in 1959.
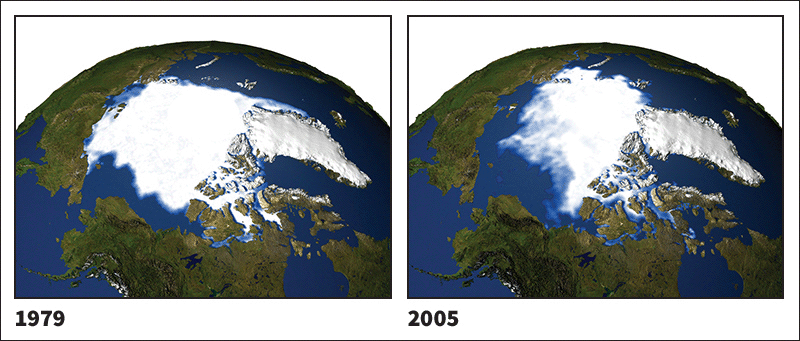
The disappearance of sea ice poses a threat to the wildlife of the Arctic Ocean. These satellite photographs show the extent of summer sea ice in 1979 (left) and 2005 (right). The ice covering has decreased as a result of global warming, an increase in the average temperature at Earth's surface. NASA
GCP scientists also calculated that the 2010 rate was almost certainly the largest yearly jump since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution in 1750. Based on these numbers, the scientists calculated that the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere has reached its highest level in the past 800,000 years. CO2 emissions had dropped slightly in 2009 because the worldwide financial crisis had reduced manufacturing. The GCP scientists calculated that about half of the emissions remained in the atmosphere. The rest was absorbed by the ocean and bodies of water on land as part of the carbon cycle.
Other highlights of the report included the following:
- China, India, and the United States led the world in CO2 emissions in 2010;
- China accounted for 24.6 percent of total emissions, compared with 16.4 percent for the United States;
- A large percentage of the emissions came from the burning of fossil fuels in power plants and factories and the production of cement;
- Annual CO2 emissions from burning fossil fuels have increased by 49 percent since 1990, the base year used by the Kyoto Protocol for calculating reductions.
Additional World Book articles:
- Global warming
- The Great Meltdown (a Special Report)
- The Ocean’s Changing Chemistry: Tipping the Balance? (a Special Report)


