The Coronavirus Epidemic
Monday, February 24th, 2020February 24, 2020
Last week, on February 19, the Wuhan coronavirus epidemic claimed its 2,000th victim. First recognized in human beings in the Chinese city of Wuhan in December 2019, the coronavirus has since spread steadily and touched nearly all parts of the world. Wuhan coronavirus is an informal name for a respiratory disease named Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Coronaviruses are one of many virus types that cause the common cold and other diseases of the upper respiratory system. The COVID-19 is a pneumonia-like disease. Its symptoms include breathing difficulties, coughing, and fever. It is a contagious disease, and the symptoms can be fatal in a small percentage of cases.
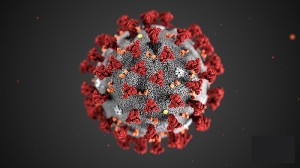
This illustration of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) shows the spikes on the outer surface of the virus that appear as a corona, giving the virus its name. Credit: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
On Jan. 30, 2020, when the disease had caused 170 deaths in some 8,000 confirmed cases, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the virus outbreak to be a public health emergency of international concern. The WHO recommended urgent containment measures as the number of cases and deaths continued to climb. By mid-February, more than 40,000 cases of the virus had been confirmed. The disease was given the temporary name 2019-nCoV, for novel (new) coronavirus of 2019. It was later officially named COVID-19. The virus that causes the disease was named SARS-CoV-2.
The first COVID-19 cases occurred near a seafood and live animal market, suggesting the disease was zoonotic (spread from animals to people). However, human-to-human transmission of the disease was later reported. Chinese medical experts confirmed that, like the related diseases MERS and SARS, COVID-19 has its origins in bats. No vaccines or drugs are available to prevent or cure the disease. Treatment of infected patients mainly involves relieving the symptoms of infection.
The coronavirus was quickly detected in areas near Wuhan. In an effort to stop the spread of the disease, Chinese authorities restricted travel in Wuhan as well as in Ezhou, Huanggang, Jingmen, Xiantao, and other nearby cities. Many public events were canceled or postponed, and intense screening for the disease was instituted at airports in China and around the world. Despite these efforts, cases were soon reported in other Asian countries, and then in other nations throughout the world. Many countries took such steps as suspending all flights to China and quarantining incoming travelers from China to prevent further spread of the virus.


