Odds of Life on Ancient Mars Just Got a Bit Better
Tuesday, December 9th, 2014December 9, 2014
Data from NASA’s Curiosity rover have revealed fascinating new details about the ancient geology of Mars, including the formation of Mount Sharp (also known as Aeolis Mons) and the abundance of surface water. The findings have also increased the likelihood that Earth may not have been the only planet in the solar system with primitive life billions of years ago.
Curiosity scientists reported that they think they have discovered why a 3-mile- (5-kilometer-) high mountain sits in the middle of Gale Crater, the impact crater where the rover landed in August 2012. Before Curiosity, scientists knew that Mount Sharp, like some mountains on Earth, consists of layer upon layer of sediment (layers of dirt, stone, and other materials laid down over many millions of years. But they did not know how Mount Sharp formed because, unlike Earth, Mars has not been shaped by plate tectonics. One theory was that the mountain formed from material that was thrown up as an asteroid or meteor crashed onto the surface there about 3.5 billion years ago. Another theory suggested that the mountain was “excavated” as sediments were eroded from around the peak. Studies made as Curiosity treks up the mountain now suggest that both wind and water were likely involved in the process.
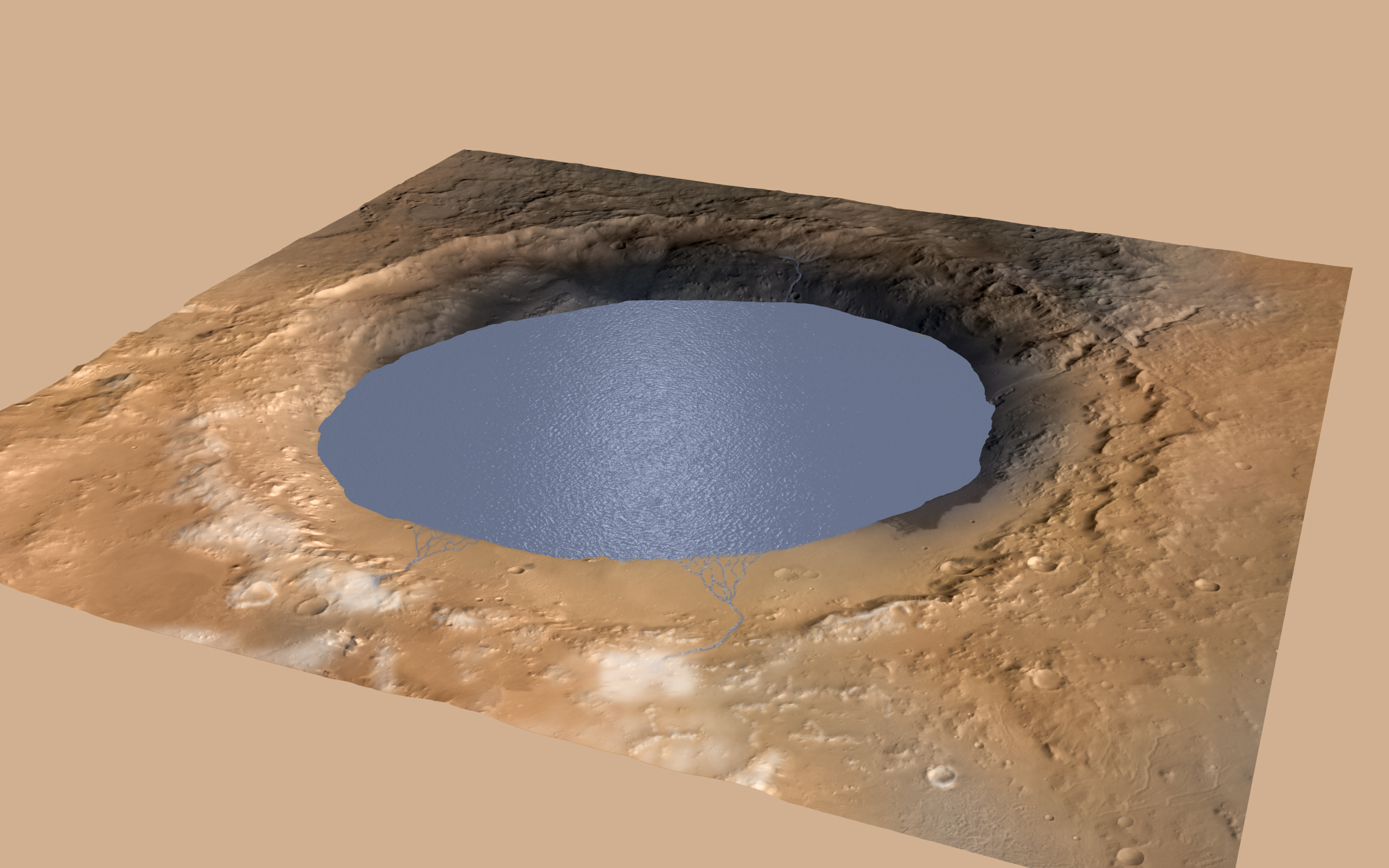
Patterns of sedimentary deposits in Gale Crater suggests the crater held a lake more than 3 billion years ago, filling and drying in cycles that lasted tens of millions of years. (NASA/JPL-Caltech/ESA/DLR/FU Berlin/MSSS)
Curiosity scientists think that Gale Crater experienced repeated wet and dry episodes that lasted for millions, or tens of millions, of years. During the wet episodes, rivers carrying water filled with sand and rock flowed over the crater’s rim to the floor, forming one large lake or even several smaller lakes. Over time, the sediments settled out of the water and hardened into layers that may have completely or partially filled the crater. During the dry episodes–when the water in the lakes evaporated–Martian winds sculpted the mountain by blowing away some of the sediment around the rim. Gradually, the mound in the center of the crater grew higher and higher.

Mount Sharp in Gale Crater likely formed from layers of sediment (yellow) carried by wind and by rivers flowing over the crater’s rim (above). The sediments then settled out in the center of the crater, forming rock (brown). Wind then eroded the sedimentary rock around the rim, forming Mount Shap. (NASA/JPL-Caltech/ESA/DLR/FU Berlin/MSSS)
The existence of surface water–as well as underground water–on Mars for such a long period–perhaps 1 billion years–increases the chances that primitive life may have developed on the planet billions of years ago. In such a stable environment, which could have lasted for some 1 billion years, life could have arisen on the red planet some 3.8 billion years ago, as it did on Earth.
Additional World Book articles:
- Mars Pathfinder
- Phoenix [spacecraft]
- Space exploration (Probes to Mars)
- The Search for Water on Mars (a Special Report)


