Ebola Outbreak in West Africa Continues to Spread
Friday, August 1st, 2014August 1, 2014
Efforts to control the Ebola outbreak in West Africa are not keeping up with the speed with which the deadly virus is spreading, World Health Organization (WHO) General-Director Margaret Chan declared today. Speaking at a summit of regional leaders, Dr. Chan warned that failure to contain the deadly disease could be “catastrophic in terms of lost lives but also severe socioeconomic disruption and a high risk of spread to other countries. . . . Cases are occurring in rural areas which are difficult to access, but also in densely populated capital cities.” However, Chan does believe that the current outbreak can be stopped, and she announced that WHO is launching a $100-million Ebola response plan in the worst affected countries–Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone.
Yesterday, Tom Frieden, the director of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), announced that the agency is sending 50 additional personnel over the next 30 days to help the 12 staff members already on the ground in West Africa. “The bottom line is that Ebola is worsening in West Africa,” he said. The announcement came after the CDC raised its travel health alert to Level 3, the highest level, for Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone. The CDC warned people to avoid nonessential travel to those countries.
According to the World Health Organization, the latest outbreak of Ebola has left 729 people dead, including top physicians in Liberia and Sierra Leone. The outbreak has also sickened two Americans–a doctor and a medical aid–who are being flown to CDC medical facilities in Atlanta. There is no vaccine to prevent the illness, and no specific treatment for it beyond attempting to nurse people through the worst of the fevers, bleeding, and other symptoms. The only way to stop an outbreak is to isolate each infected patient and trace all of his or her contacts and isolate them in turn.
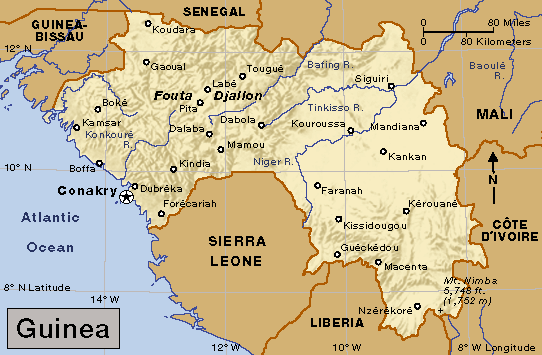
The current outbreak of Ebola fever began in southern Guinea and quickly spread to Liberia and Sierra Leone. (World Book map; map data © MapQuest.com, Inc.)
Lansana Gberie, a prominent scholar from Sierra Leone, has condemned his government’s response to the outbreak: “The whole thing has been very incompetently handled. If the government had quarantined this area [in remote northwestern Sierra Leone] they could have contained it. Instead they opened a treatment center in Kenema, a major population center.”
Two of the three affected countries have begun to respond to the crisis. Sierra Leone has declared a public health emergency, and the president, Ernest Bai Koroma, has ordered security forces deployed to support health professionals. “All epicenters of the disease will be quarantined,” said Koroma, along with “localities and homes where the disease is identified and searched for infected people.” Public meetings are restricted, and he ordered top officials to cancel all but essential overseas travel.
In Liberia, the government has closed most border crossings and ordered the deployment of security forces to combat the outbreak. Public gatherings have been banned and schools closed. Nonessential government workers have been put on compulsory leave for 30 days.
Additional World Book articles:
- Africa 1995 (a Back in Time article)
- Africa 1996 (a Back in Time article)
- Uganda 2012 (a Back in Time article)
- The Origin of New Diseases (a special report)